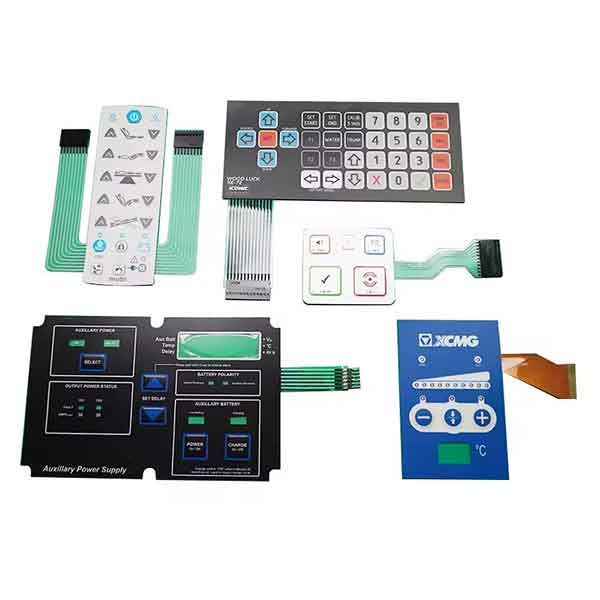
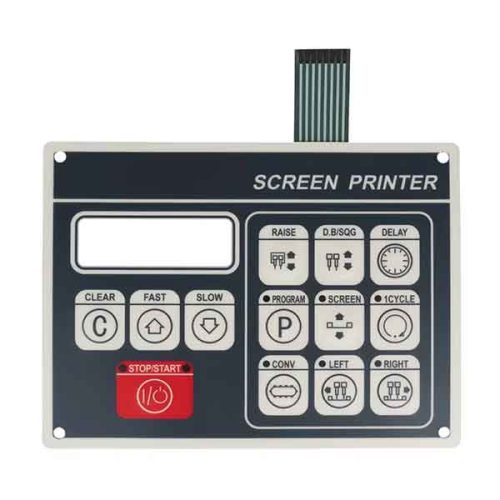
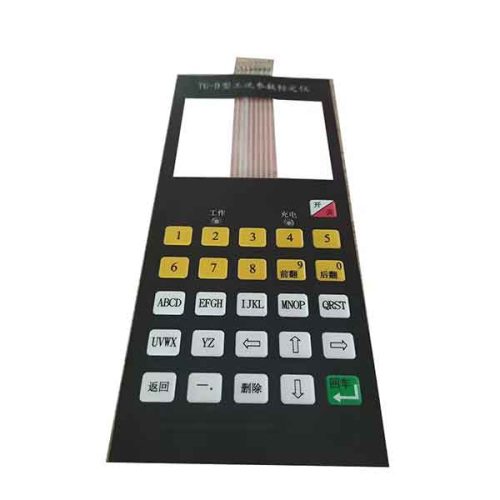
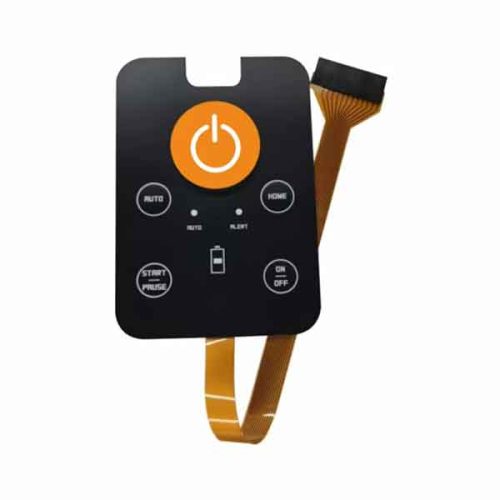
Membrane Switch keypads are well-suited for portable medical electronics and require high visibility. Membrane switches are particularly suitable for handheld medical applications and portable devices because they are lightweight, low profile, durable, easy to clean, and RoHS-compliant.
Waterproof Membrane Switch
Description
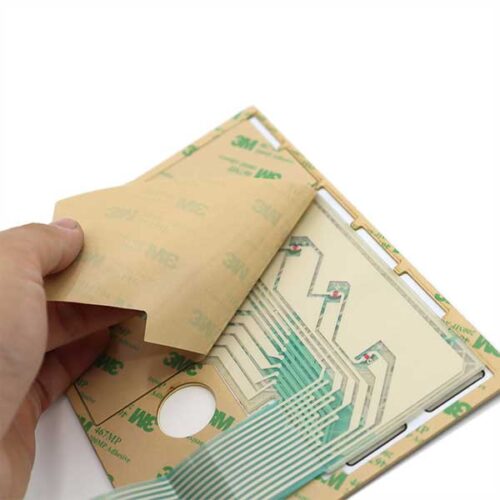
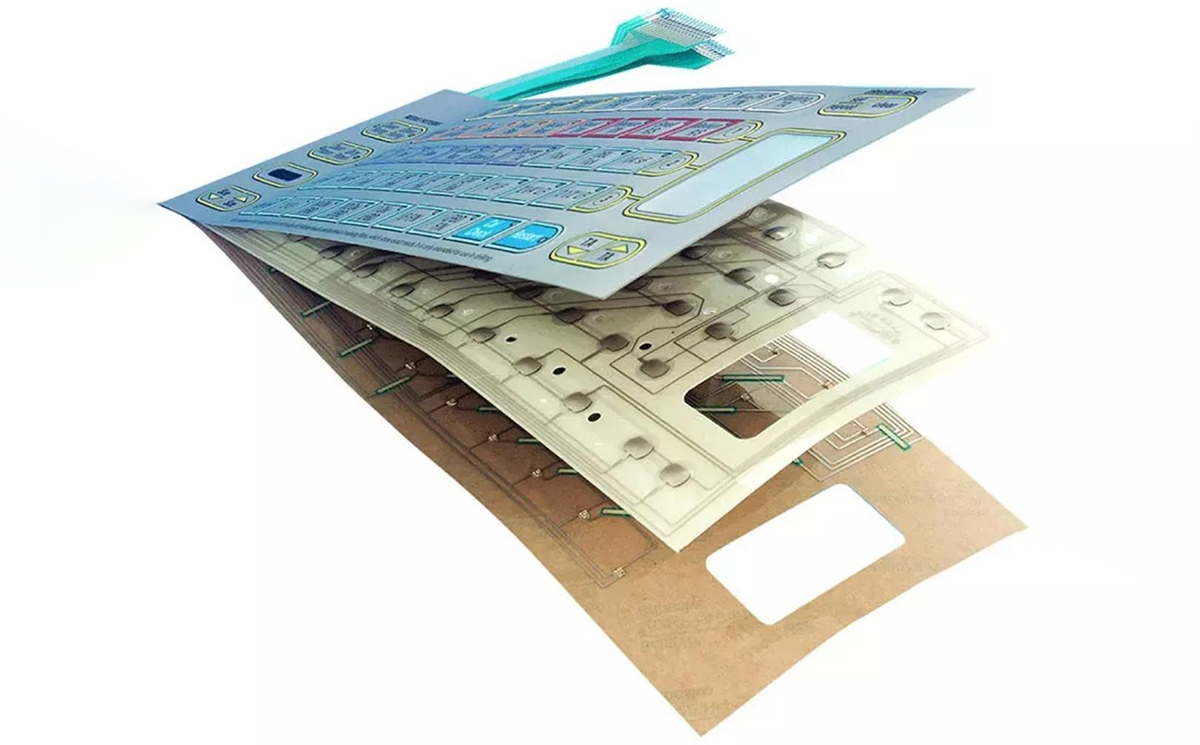
Membrane switches offer numerous design options that enable manufacturers to develop appropriate interfaces that link the end user to the machine’s functionality. A typical membrane switch assembly contains several layers which all serve a distinct purpose for the entire membrane switch, these layers include:
- Graphic overlay- 0.15/0.20mm
- Overlay adhesive-0.1/0.2mm
- Top circuit layer-0.1mm
- Circuit spacer-0.1/0.2mm
- Lower circuit layer-0.1mm
- Rear adhesive layer-3M 467 468
- Rigid support layer-Custom demand
Key Features
- Embossing button
- Circuit encoding
- Hard coat finishes
- Tactile feedback
- Tinted windows
- LED Backlighting
- Panel interconnections
- Subpanels
- Elastomer keypads
FAQ Guide
In today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world, membrane switches have become a ubiquitous component in electronic devices. This comprehensive FAQ guide will explore the essential aspects of waterproof membrane switches, including their types, advantages, disadvantages, troubleshooting methods, and applications. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of waterproof membrane switches and their significance in modern electronics.
1. What is a Waterproof Membrane Switch?
A waterproof membrane switch is a type of user interface designed to operate in environments where exposure to water, moisture, or other liquids is a concern. Unlike traditional membrane switches, which may be susceptible to damage from liquids, waterproof membrane switches are specifically engineered to prevent water ingress and maintain functionality even in wet or humid conditions.
The construction of a waterproof membrane switch typically involves multiple layers, including a graphic overlay, a spacer, a circuit layer, and a backing layer. What sets these switches apart is the use of specialized sealing techniques, such as adhesive gaskets, perimeter seals, or conformal coatings, to create a waterproof barrier. This ensures that the switch remains fully operational even when exposed to water or other liquids.

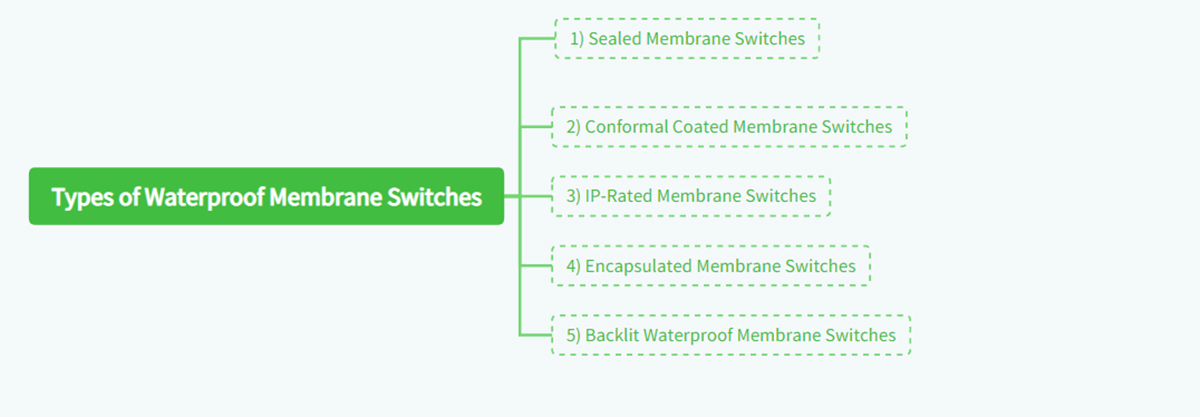
2. Types of Waterproof Membrane Switches
Waterproof membrane switches come in several different types, each designed to meet specific application requirements. Understanding the various types can help you choose the most suitable switch for your particular needs.
1) Sealed Membrane Switches
Sealed membrane switches are the most common type of waterproof membrane switch. These switches use adhesive gaskets or perimeter seals to create a watertight barrier around the switch layers. The sealing prevents water from entering the switch and damaging the internal circuitry. Sealed membrane switches are often used in applications where the device may be exposed to splashes, rain, or high humidity.
2) Conformal Coated Membrane Switches
In conformal-coated membrane switches, a protective coating is applied to the circuit layer to shield it from moisture and contaminants. The conformal coating is typically made from materials such as silicone, acrylic, or polyurethane, which provide excellent resistance to water and other environmental factors. These switches are ideal for applications where the switch may come into direct contact with water or other liquids.
3) IP-Rated Membrane Switches
IP-rated membrane switches are designed to meet specific **Ingress Protection (IP) ratings**, which indicate the level of protection against solid particles and liquids. For example, an IP67-rated membrane switch is fully protected against dust and can withstand immersion in water up to a certain depth for a specified period. IP-rated waterproof membrane switches are commonly used in outdoor applications, such as marine equipment or industrial control panels.
4) Encapsulated Membrane Switches
Encapsulated membrane switches are fully enclosed in a protective casing, which provides an additional layer of protection against water, dust, and other environmental hazards. The encapsulation ensures that the switch remains functional even in the harshest conditions, making it suitable for extreme environments such as military or aerospace applications.
5) Backlit Waterproof Membrane Switches
Backlit waterproof membrane switches incorporate lighting elements, such as LEDs or fiber optics, to illuminate the keys. This feature is particularly useful in low-light or outdoor environments where visibility is essential. The backlighting is fully integrated into the waterproof design, ensuring that the switch remains sealed and protected from moisture.
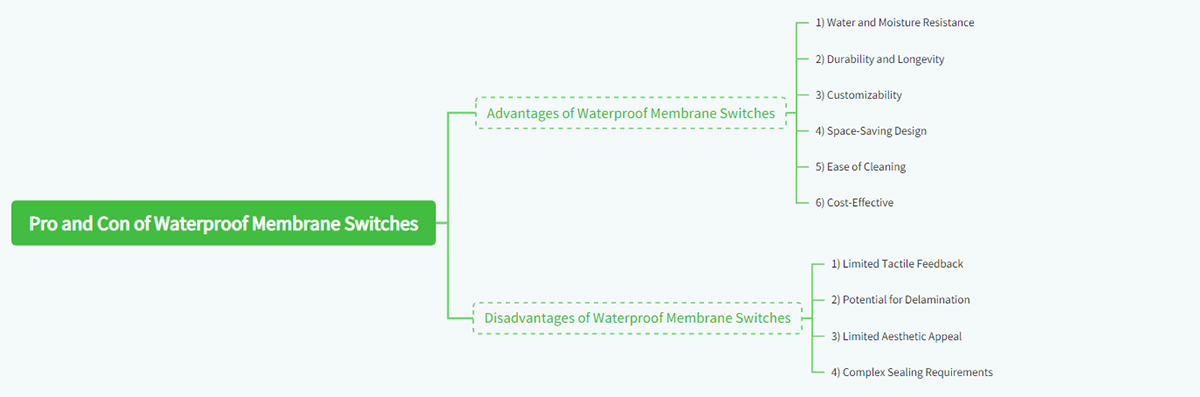
3. Advantages of Waterproof Membrane Switches
Waterproof membrane switches offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for a wide range of applications. Below are some of the key benefits:
1) Water and Moisture Resistance
The most obvious advantage of waterproof membrane switches is their ability to resist water and moisture. These switches are designed to operate reliably in wet or humid environments, making them ideal for applications where exposure to liquids is a concern. Whether used in outdoor equipment, medical devices, or industrial machinery, waterproof membrane switches provide peace of mind that the device will continue to function even in challenging conditions.
2) Durability and Longevity
Waterproof membrane switches are built to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including exposure to water, dust, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. The sealed construction and use of durable materials ensure that these switches have a long lifespan, even in demanding applications.
3) Customizability
Like other membrane switches, waterproof versions can be fully customized to meet the specific needs of a device or system. The graphic overlay can be printed with custom colors, symbols, and logos, allowing for a high degree of personalization. Additionally, the tactile feedback, backlighting, and sealing methods can be tailored to suit the application’s requirements.
4) Space-Saving Design
Waterproof membrane switches are thin and lightweight, making them ideal for applications where space is limited. Their compact design allows them to be integrated into devices without adding significant bulk, making them a preferred choice for modern electronics.
5) Ease of Cleaning
The smooth, sealed surface of waterproof membrane switches makes them easy to clean and sanitize. This feature is particularly important in industries such as healthcare, food processing, and pharmaceuticals, where hygiene is a top priority. The sealed design prevents water, cleaning agents, and disinfectants from entering the switch, ensuring that it remains functional even after repeated cleaning.
6) Cost-Effective
Compared to other waterproofing methods, such as mechanical seals or enclosures, waterproof membrane switches are relatively cost-effective to produce. Their simple construction and the use of inexpensive materials make them an economical choice for manufacturers, especially when produced in large quantities.
4. Disadvantages of Waterproof Membrane Switches
While waterproof membrane switches offer numerous benefits, they are not without their drawbacks. Below are some of the potential disadvantages:
1) Limited Tactile Feedback
One of the main limitations of waterproof membrane switches is that they may offer less tactile feedback compared to mechanical switches. While some waterproof membrane switches are designed with tactile domes to provide a “click” sensation, the feedback may not be as pronounced as in traditional mechanical switches. This can be a disadvantage in applications where strong tactile confirmation is required.
2) Potential for Delamination
Over time, the layers of a waterproof membrane switch may begin to separate, a process known as delamination. This can occur due to prolonged exposure to heat, moisture, or chemicals, and may lead to reduced functionality or failure of the switch. While proper sealing techniques can minimize the risk of delamination, it is still a potential concern in some applications.
3) Limited Aesthetic Appeal
While the graphic overlay of a waterproof membrane switch can be customized, the overall appearance may not be as visually appealing as other types of interfaces, such as touchscreens or mechanical keyboards. For applications where aesthetics are a priority, waterproof membrane switches may not be the best choice.
4) Complex Sealing Requirements
Achieving a truly waterproof design requires precise sealing techniques and materials. If the sealing is not done correctly, water ingress can occur, leading to the failure of the switch. This makes the manufacturing process more complex and may increase production costs in some cases.
5. Troubleshooting of Waterproof Membrane Switches
Like any electronic component, waterproof membrane switches can experience issues over time. Below are some common problems and troubleshooting steps:
1) Unresponsive Keys
If one or more keys on the switch are unresponsive, the issue could be due to a broken circuit or a faulty dome. In this case, the switch may need to be disassembled and inspected for damage. If the dome is damaged, it will need to be replaced. Additionally, check for any water ingress that may have compromised the internal circuitry.
2) Water Ingress
If water has entered the switch, it may cause the switch to malfunction. Inspect the sealing around the switch layers to ensure that it is intact. If the seal is damaged, the switch may need to be replaced or resealed. In some cases, drying out the switch and resealing it may restore functionality.
3) Reduced Tactile Feedback
If the tactile feedback has diminished, the domes within the switch may be worn out. Replacing the domes or the entire switch may be necessary to restore proper functionality. Additionally, ensure that the switch has not been exposed to excessive moisture, which can affect the tactile response.
4) Delamination
If the switch layers are separating, the switch may need to be replaced. Delamination can occur due to prolonged exposure to heat, moisture, or chemicals, so it’s essential to ensure that the switch is used in appropriate conditions. Preventive maintenance, such as regular inspections, can help identify delamination before it leads to failure.
6. Applications of Waterproof Membrane Switches
Waterproof membrane switches are used in a wide range of industries and applications due to their versatility and durability. Below are some of the most common applications:
- Medical Devices: devices such as diagnostic machines, patient monitoring systems, and handheld medical instruments
- Outdoor Equipment: Marine electronics, weather monitoring devices, and outdoor control panels
- Industrial Control Panels: Factories, warehouses, and other demanding environments
- Consumer Electronics: remote controls, kitchen appliances, and outdoor gadgets
- Aerospace and Military Applications
7. Conclusion
By understanding the types, advantages, disadvantages, and troubleshooting methods of waterproof membrane switches, you can make informed decisions about their use in your projects. With their wide range of applications and proven reliability, waterproof membrane switches are sure to remain a vital component in the world of electronics for years to come.







