In case you are looking for a full sheet adhesive label, you may discover that there are quite a few different kinds, none of which relate to the label but to the back of the sheet. Why would there be so many and what purpose do they fulfill? Below, we look at the purpose of back slits and why every model is ideal for different projects.
1. What are Full Sheet Labels?
Full sheet labels refer to one-piece adhesive sheets that are of sufficient size to cover an entire A4, Letter, or custom-sized backing sheet without being pre-cut to various shapes. Contrary to die cut labels which come in fixed sizes, full sheet labels have a completely blank surface on which the user can print, design, and cut their own shape and sizes of choice.
They are typically built from paper, vinyl, or polyester substrates covered with a variety of adhesives such as permanent, removable, or repositionable adhesives to support a wide variety of applications. Complete sheets of labels can be utilized on inkjet or laser printers and are therefore well-suited both for in-office applications and professional production houses.
In general, full sheet labels offer total versatility. You can make shipping labels, product labels, identification tags, or promotion decals all from the same sheet by simply printing and cutting them to your desired sizes.

2. Materials of Full Sheet Labels
Material choice is likely the most important decision while buying full sheet labels. Each material provides unique textures, durability and printability properties; becoming aware of this allows you to select the ideal type for your application.
1. Paper Labels
Paper is the least expensive and most versatile option. It produces great prints and can be used for short-term indoor applications such as address labels, product description stickers, or packaging.
Matte or gloss finish is available in paper labels and are easy to write on. They are not resistant to water, oil, or high humidity.
Applications for: general office use, product packaging, and mailing labels.
2. Vinyl Labels
Vinyl labels are waterproof and tear-resistant with a flexible, durable surface. They can be applied to slightly curved as well as smooth surfaces. Vinyl stocks can be printed on inkjet or laser printers and applied outside for an extended period of time.
Due to its weatherproof and smooth finish, this material makes for ideal applications exposed to moisture or sunlight.
Ideal for product and equipment labeling as well as outdoor labels.
3. Polyester (PET) Labels
Polyester (PET) Labels Polyester labels are stronger and heat-resistant than paper or vinyl labels, making them suitable for harsh environments where friction, chemicals or heat may be present. Furthermore, PET material resists color fading and adhesion loss even under challenging circumstances.
These labels feature professional glossy or matte coating and are widely used for electronic or industrial products.
Excellent choice for: warning stickers, electronics and high-performance labels.
4. Clear or Transparent Labels
Translucent labels are created from clear vinyl or polyester film. They create a “no-label look,” meaning the background or product surface is still visible. This is utilized for cosmetics, glass jars, and upscale product packaging.
Pigment ink or laser toner is required to print on clear material to create vibrant, durable colors.
Recommended for: packaging decorations, bottles, and branding surfaces.
5. Specialty Materials
For specialty or premium applications, manufacturers also offer specialty materials such as:
- Water-resistant synthetics for boating or outdoor applications
- Removable and repositionable films for promotional signs and recycled paper for eco-friendly brands
- Each of these can be applied using different adhesives and coatings to optimize performance and appearance.
Briefly, material selection depends on where and how a label will be used. Paper is cost-effective for indoor purposes while vinyl and polyester provide durability benefits while clear films present an elegant high-end appearance to increase brand visibility.
3. Production and Manufacturing Workflow of Full Sheet Labels
The production of full sheet labels involves a series of precise and well-controlled processes. Each step affects the label’s final appearance, adhesion, and print quality. Understanding this workflow helps buyers estimate lead times and evaluate the technical capacity of a manufacturer.
1. Material Preparation
The process starts with the choice and preparation of the base material, e.g., paper, vinyl, or polyester film. The selected substrate is wound onto wide rolls, washed, and treated to provide even surface adhesion during the coating process.
The manufacturers also check the material for thickness, flatness, and surface cleanliness to prevent defects in printing at a later stage of production.
2. Adhesive Coating
A coat of adhesive is evenly applied on the backside of the material by a coating machine. Dependent upon its use, labels may require either permanent, removable, or repositionable adhesives.
Distributing adhesive evenly will create even bonding strength.
3. Liner Application
Once the adhesive layer has set, a release liner (or silicone-coated liner) is laminated onto it to keep any glue from adhering until applied to a label. This helps ensure an even application of glue across each label surface.
This ensures labels can be printed, stored, and handled without sticking prematurely.
4. Printing Process
The coated substrate is subsequently printed with the intended graphics, logos, or text. It may be printed digitally, flexographically, or offset, based on order quantity and design complexity.
Color accuracy, resolution, and registration are closely tracked.
5. Surface Finishing
After being printed, labels can then be given optional surface finishes such as gloss, matte or protective UV coating for increased durability, scratch resistance and overall aesthetic appeal. These coatings also serve to increase longevity as well as scratch resistance.
Others, particularly high-end brands, will receive lamination to improve waterproofing capabilities or create an upscale tactile experience.
6. Sheet Cutting and Trimming
The rolls are cut into separate sheets in A4, Letter, or bespoke sizes. Precision cutting ensures neat label edges and well-aligned edges for printer compatibility.
The whole sheet labels at this stage are inspected to ensure that there is no folding, misalignment, or surface contamination.
7. Quality Inspection
Before being packaged for sale, all lots undergo a final check to assess print quality, adhesion strength, color consistency and sheet size. Manufacturers use routine testing techniques like peel tests, visual inspection and sample print testing trials to monitor performance.
8. Packaging and Storage
Filled-out sheets are stacked, shrink-wrapped, or boxed with moisture-proof film to prevent curling or adhesive contamination. Export orders are flat-packed in corner protection cartons in a manner that preserves the sheet’s shape during transportation.
Short, in summary, full sheet label printing is not just a printing process but a whole process that incorporates materials science, precise coating, and quality control. Each process results in the creation of labels that are easy to apply, print, and store with constant performance and appearance.

4. How to Print on Full Sheet Labels?
Printing full-sheet labels is an easy and professional-quality solution to meet all of your labelling needs. Just follow this step-by-step guide for success:
1) Printer Compatibility
Both inkjet and laser printer types are compatible with full sheet labels. The proper label type should be selected for the intended printer to avoid smudging or destruction of the printer.
2) Template Usage
Most label makers include templates that will be usable with top word processing and graphics computer software, such as Microsoft Word, Adobe Illustrator, and Photoshop. Templates simplify the design and positioning process of your labels.
3) Design Considerations
- Bleed Area: Include a bleed area in the design so that white margins are avoided when cutting.
- Resolution: Use high-resolution images and text so that the labels look professional and clear.
- Alignment: Print a test page on regular paper to check alignment before using the actual label sheet.
4) Printing Tips
- Load a single sheet at a time in the printer to prevent jamming.
- Select the proper paper type setting, such as “Labels” or “Heavy Paper.”
- After printing is complete, be careful not to touch or disturb the printed area immediately post-printing to avoid smudging and prevent inkjet printer smudging issues.
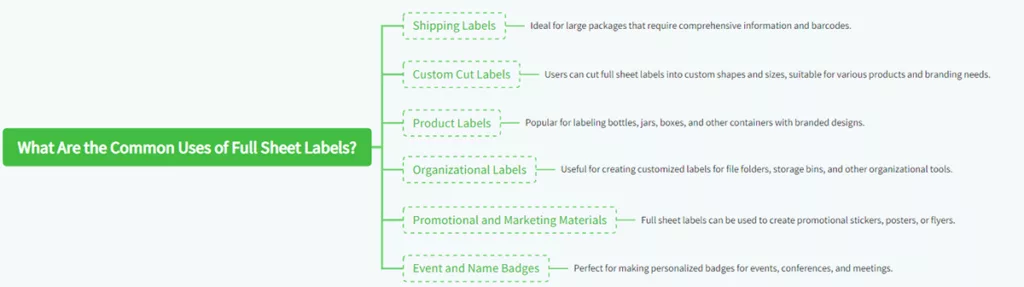
5. What Are Common Applications of Full Sheet Labels?
Full sheet labels are very diverse and can be used for any number of functions in both the home and corporate settings. Here are some popular applications of full sheet labels:
- Shipping Labels: Most appropriate for big packages where detailed information and barcodes will be required.
- Custom Cut Labels: Full sheet labels can be cut into custom size and shape according to the various products and brand needs.
- Product Labels: Famous for embellishing bottles, jars, boxes, and other containers with branded motifs.
- Organizational Labels: Ideal for creating custom labels for file folder labels, storage bin labels, and other organizing materials.
- Promotional Materials: The whole sheet labels can also be used to create advertisements stickers, billboards, or leaflets.
- Event and Name Badges: Suitable for creating customized badges for meetings, conferences, and events.
6. How to Choose the Proper Full Sheet Labels for Your Purpose?
When selecting the right full sheet labels perfect for your uses, you have to consider a few things to enable you to make the correct choice. Check out the following tips for reference:
1) Material Selection
- Matte Finish: Its finish is not-glare type that is more ideal for using in normal office applications.
- Glossy Coating: Gives a shiny professional look, best suited for promotional products and high-grade product labels.
- Weatherproofing and Water resistance: Applied for external purposes or in more-heavy usage where the weather resistance is of utmost importance.
- Clear coating: Transparent labels which become a full part of the surface they are attached to, and are therefore well-suited for simple designs.
2) Adhesive Type
- Permanent: Perfect for labels which are meant to be permanent and should not come off without getting torn.
- Removable: Best for peel off labels that will not leave residue behind.
- Repositionable: Allows moving the location of the label multiple times during application.
- High-Tack: Provides super-strong adhesion to tricky surfaces like textured or rough material.
3) Printer Compatibility
Make the entire sheet labels compatible with either laser or inkjet printers, since the combination of wrong label type and wrong printer can lead to poor print quality or damage to printer/label.
4) Environmental Considerations
- Temperature Resistance: Test for labels that can withstand very high or low temperatures if they will be used at these temperatures.
- Moisture Resistance: Waterproof labels are necessary for water-exposed or humid products.
7. How to Correctly Apply Full Sheet Labels?
To have a smooth and successful application of full sheet labels, there are right steps to be followed to achieve a professional and finished appearance. Here’s a guide on how to apply full sheet labels correctly:
1) Surface Preparation
Clean and dry the surface where the label will be applied to have no dust, grease, or other debris that may prevent adhesion.
2) Application Technique:
- Peel and Stick: Gradually peel the backing of the label off carefully and apply it from one edge to the other edge, smoothing simultaneously to eliminate bubbles and wrinkles.
- Smooth Out Bubbles: Smooth air bubbles caught under the label with a squeegee or a flat tool.
- Overlap Edges: Overlap edges of label sheets slightly for large surfaces if over one sheet is needed.
3) Repositioning
If removable or repositionable labels are employed, lift and replace carefully if the position needs to be changed. Ensure no edge or corner is raised, since this will result in peeling over time.
4) Environmental Conditions
Apply labels at room temperature and avoid exposure to moisture until the adhesive has fully set.
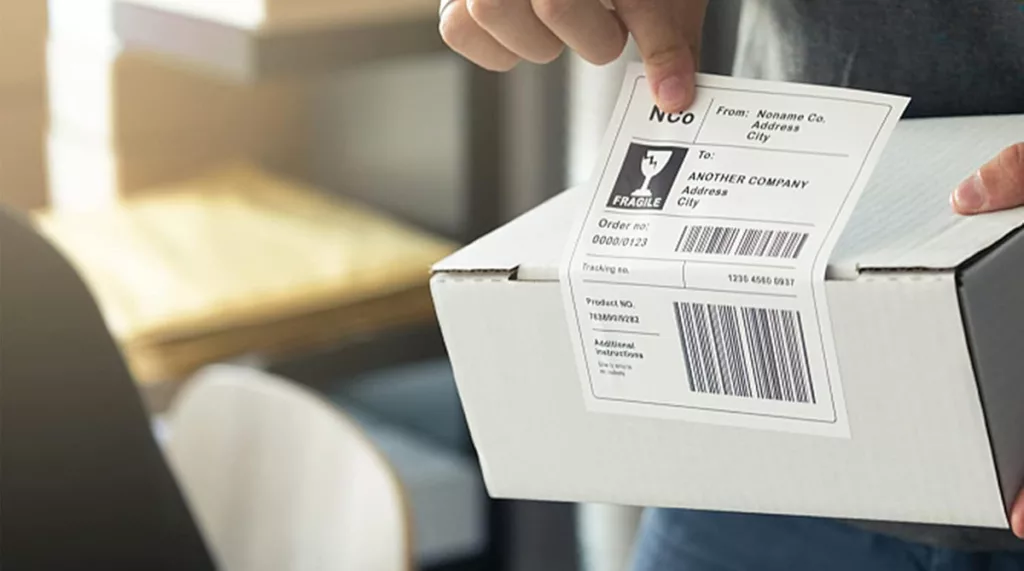

8. Troubleshooting and Common Problems of Full Sheet Labels
Using full sheet labels can be followed by some common problems that may affect the overall appearance and stickiness of the labels. Some common problems and troubleshooting procedures you can follow to effectively address them are listed below:
1) Printing Misalignment
Use manufacturer-provided templates and print a test page before printing on the label sheet. Adjust the settings in the printer software to ensure alignment.
2) Ink Smudging
Ensure you are using the correct label type for your printer (inkjet or laser). Allow the ink to dry completely before handling the printed labels.
3) Label Peeling Off
Check if the surface is clean and suitable for adhesive labels. Use stronger adhesive labels if necessary.
4) Bubbles and Wrinkles
Slowly place the label onto one side and smooth the label direction. Use machines like a squeegee to remove air bubbles.
5) Printer Jamming
Load one sheet at a time and ensure the printer settings match the label type (e.g., “Labels” or “Heavy Paper”). Check the printer manual for guidance on label printing.
9. How to Keep Printed Full Sheet Labels?
To keep the quality and shelf life of printed full sheet labels optimal, proper care and handling procedures must be followed. Here are the ways on how to properly take care of printed full sheet labels:
- Handling: Handle the labels from the edges in order not to smudge them. Don’t touch the adhesive side to prevent contaminating them.
- Storage: Keep label sheets stored away in a cool and dry area in order to avoid warping or curling.
- Exposure: Avoid direct sun light, heat and water for the best results and to reduce peeling or fading of labels.
- Cleaning: If necessary, dust the label surface using a moist cloth but do not use harsh cleaners which could compromise its print.
10. Customization and Special Features
Whenever it is a question of complete sheet labeling, the possibilities are endless! Here is how you can add additional features and customize your labels to give them a personal touch:
- Custom Shapes: Through the use of full sheet labels, end-users have the capability to custom-cut any size and shape for specific application.
- Design Software: Employ software for designing which provides a range of tools for customizing such as Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, or web-based label design software provided by label manufacturers.
- Variable Data Printing: Full sheet labels are best utilized in variable data printing where each label will need to be different, i.e, sequential barcodes, addresses, or personalized information.
- Eco-Friendly Options: Use green materials such as recycled paper labels or biodegradable adhesives in order to meet environmental regulations and appeal to green consumers.
11. Quality Control and Testing Standards of Full Sheet Labels
Quality control is an essential part of full sheet label production. Each sheet must meet strict standards for appearance, adhesion, and print performance to ensure consistent results across large batches. Reliable manufacturers perform several inspections and tests before delivery.
1. Visual Inspection
- Every production batch begins with a detailed visual check.
- Operators examine the sheet surface under bright lighting to ensure there are no defects such as dust particles, scratches, color spots, or coating streaks.
- Labels are also inspected for even color tone and alignment accuracy between print layers.
Key checks:
- Smooth and uniform surface
- No visible bubbles, wrinkles, or curling
- Clear and sharp printing without color bleeding
2. Dimensional Accuracy
- Full sheet labels must fit standard printers and cutting tools.
- Each batch is measured for sheet size, edge straightness, and thickness consistency.
- Typical dimensional tolerances are within ±0.2 mm, while thickness deviation is kept under ±0.05 mm.
Purpose: to ensure smooth feeding through printers and prevent jamming or misalignment during user printing.
3. Adhesion and Peel Strength Tests
The adhesive layer determines how well the label sticks to different surfaces.
Manufacturers test peel strength using standardized test tapes and controlled pulling angles.
Common procedures include:
- Peel test at 180 degrees to measure adhesive force
- Reposition test for removable labels to ensure clean removal without residue
- Surface compatibility test on plastic, metal, glass, and cardboard substrates
- Adhesion performance is usually verified according to ASTM D3330 or FINAT testing standards.
4. Print Durability and Ink Adhesion
- To confirm that printed designs remain clear over time, the labels undergo durability testing.
- A sample sheet is rubbed with a soft cloth or soaked in water to check for ink fading or smearing.
- Some manufacturers also perform alcohol resistance and UV exposure tests to evaluate long-term color stability.
Key evaluations:
- No color transfer after rubbing test
- No visible fading after 24-hour light exposure
- Stable printing under humidity or temperature changes
5. Surface Coating and Lamination Testing
- If the label has gloss, matte, or UV coating, the coating layer is checked for uniformity and hardness.
- A pencil hardness test (commonly rated from HB to 3H) is used to measure scratch resistance.
- For laminated sheets, manufacturers test lamination adhesion to ensure no air pockets or edge lifting.
6. Environmental Resistance Tests
High-quality full sheet labels should remain functional in various conditions.
Tests may include:
- Temperature cycling from -10°C to 70°C
- Humidity resistance (95% RH for 48 hours)
- Water immersion to check adhesive stability
- Chemical exposure to verify resistance against oil, detergent, or alcohol
- Labels that pass these tests maintain their adhesion and color even in harsh industrial or outdoor settings.
7. Curling and Flatness Check
Since full sheet labels must feed smoothly through printers, flatness is a key inspection point.
Sheets are placed on a flat surface for several hours to confirm that there is no curling or warping caused by moisture imbalance or coating stress.
This ensures compatibility with both inkjet and laser printing systems.
8. Packaging and Handling Verification
Before shipment, each stack is carefully packed and tested for moisture protection.
Manufacturers perform random drop tests or vibration tests to confirm that the sheets remain undamaged during transportation.
Proper labeling and documentation ensure traceability of every batch.
9. Final Quality Report
Reputable manufacturers provide a quality inspection report summarizing all key results:
- Material batch number
- Adhesive type and peel strength values
- Visual and dimensional inspection data
- Printing and coating test results
This report helps you verify compliance with agreed specifications before accepting shipment.

12. Cost and Pricing Factors for Full Sheet Labels
The cost of producing full sheet labels varies depending on several key factors. Understanding these factors helps buyers estimate budgets more accurately and choose the most efficient production options.
1. Material Type
- The choice of base material greatly affects the total price.
- Paper is the most affordable option and is suitable for general indoor use.
- Vinyl is more expensive because it offers waterproof and tear-resistant properties.
- Polyester (PET) costs slightly more than vinyl due to its superior heat and chemical resistance.
- Specialty materials, such as clear films or eco-friendly synthetics, also add to the total cost.
2. Adhesive Selection
- Different adhesives serve different purposes and have different price levels.
- Permanent adhesive is the standard choice and provides strong bonding at a low cost.
- Removable or repositionable adhesives cost more because they use advanced formulations that allow repeated applications.
- High-tack adhesives are the most expensive option, often used for rough or textured surfaces.
3. Printing Method
- The printing process you choose also influences the price.
- Digital printing is best for small batches or custom designs but has a higher cost per sheet.
- Flexographic or offset printing is more cost-effective for large orders, although it requires setup charges for printing plates.
- The number of colors, ink type, and coating layers all affect overall pricing.
4. Surface Finishing and Coating
- Adding finishing treatments improves appearance and durability but increases cost.
- Common options include gloss or matte varnish, lamination, UV coating, and protective overlays.
- For waterproof or scratch-resistant labels, extra coating steps are often necessary, which slightly extend production time and cost.
5. Order Quantity
- Like most printed products, larger quantities lower the unit price.
- Small orders require setup and calibration time that cannot be shared across batches, while high-volume production allows manufacturers to spread costs more efficiently.
- For example, ordering 100 sheets may cost three to four times more per piece than ordering 1,000 sheets.
6. Size and Customization
- Standard A4 or Letter-sized sheets are usually cheaper because materials and packaging are optimized for these dimensions.
- Custom sizes, special die-cut shapes, or printed guides for later trimming can raise costs slightly.
- Custom packaging and labeling for resale will also increase total expenses.
7. Packaging and Logistics
- Shipping and packaging are small but important cost components.
- Moisture-proof wrapping, flat carton packaging, and international shipping protection add a minor surcharge, especially for export orders.
- Express delivery or special labeling instructions can further affect pricing.
8. Typical Price Range (for reference)
| Material Type | Printing Option | Approximate Price per Sheet (bulk order) |
| Paper (matte or gloss) | Unprinted | USD 0.05 – 0.15 |
| Vinyl | Full-color print | USD 0.20 – 0.40 |
| Polyester (PET) | Full-color + coating | USD 0.40 – 0.80 |
| Clear or specialty film | Premium finish | USD 0.80 – 1.50 |
(Prices vary depending on order quantity, size, and supplier capabilities.)
9. Tips for Cost Optimization
- Use standard sheet sizes whenever possible.
- Group multiple designs on one print layout to reduce setup costs.
- Choose paper labels for short-term indoor use and vinyl or PET for long-term projects.
- Order in bulk to take advantage of volume pricing.
- Request a sample before large-scale production to confirm performance and avoid reprints.
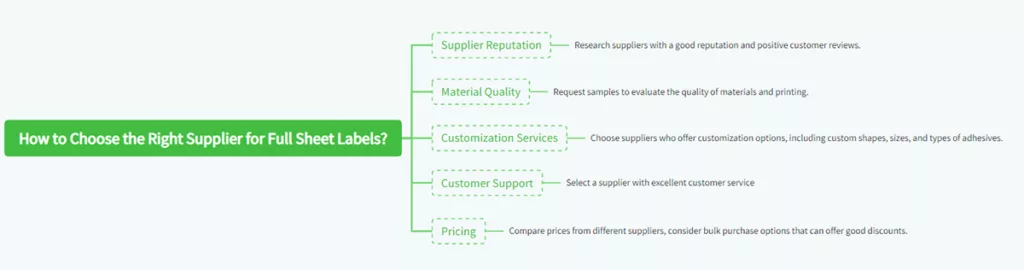
13. Full Sheet Labels Supplier Selection Tips
The proper selection of a supplier for full sheet labels is critical to meet the quality, customization, and service needs. Some of the primary considerations during the selection of a supplier for full sheet labels are as follows:
- Supplier Reputation: Search for suppliers with a good reputation and positive customer reviews. Look for companies specializing in labels with a history of satisfied customers.
- Material Quality: Request samples to check material and printing quality. Ensure the labels meet your standard before ordering in bulk.
- Customization Services: Choose suppliers offering customization services, including custom shapes, sizes, and adhesive types.
- Customer Support: Choose a supplier with excellent customer service, both technical support and template usage and printing support.
- Pricing: Prices from different suppliers must be compared but ensure that you do not compromise on quality at the expense of a lower price. Bulk purchase options that can offer good discounts must be opted for.
14. Conclusion
Full sheet labels provide unprecedented flexibility and personalization for a variety of applications. Knowing their applications, how to print and apply them, and how to select the correct type for certain requirements can actually improve your labelling work. Good maintenance and troubleshooting can guarantee durable, professional-grade labels. When selecting a supplier, search for reputation, material quality, and customer service so that you get the best from your investment. Full sheet labels, for personal, business, or industrial use, provide a practical and effective answer to all your labeling needs.




Leave A Comment