Whenever we shop, we always tend to notice barcodes, but they pass through us most of the time. Nevertheless, barcodes have a significant contribution in making our economy work efficiently and effectively, not only for small businesses, but also for massive multinational companies.
1. What are barcode labels?
Barcode labels are formal symbols that carry information in machine-readable form. Barcode labels are greatly used for identification, tracing, and stock control in applications and industries. Label creation is the process of designing and printing labels with barcodes and supporting information. An optimally designed label has the potential to enhance the speed, accuracy, and security of barcode scanning and data processing operations.

2. Barcode Label Materials and Printing Methods
Choosing the right material and printing method is important in designing durable barcode labels that can be read and are cost-effective. The printing technology and substrate of the label will decide how much the barcode will function under heat, humidity, and handling stress.
1) Common Label Materials
Paper Labels:
Paper is the least expensive and most widely available label stock. It is good quality and works well for indoor or short-duration use for products such as retail pricing, shipping tags, product inventory stickers, and certificates. Paper works poorly in indoor moisture, oil, or abrasion environments.
Synthetic Labels:
Synthetic materials such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polyester (PET), and vinyl are stronger and elastic than paper. They are resistant to tears, chemicals, and medium sunlight exposure. These are therefore suitable for industrial, logistics, and outdoor purposes.
Thermal Labels:
Thermal paper has an implanted heat-sensitive coating that changes color when exposed to heat from the printer head. It does not need to be written with ink or ribbon but is simpler to print with. There are two types, direct thermal and thermal transfer. Direct thermal labels are most appropriate for short-term applications, whereas thermal transfer labels provide more longevity when utilized in combination with ribbon ink.
High-Temperature and Specialty Materials:
For heavy use such as automotive or component electronics manufacturing, materials like polyimide or aluminum-coated film are used to resist heat, solvents, and extended exposure without degrading.
2) Comparison of Printing Technologies
Direct Thermal Printing:
This method uses heat paper, printing through direct contact with the print head. It is simple, cheap, and convenient, but the printout will be bleached after being exposed to sunlight or heat, and is therefore well suited for temporary labels such as shipping or logistics use.
Thermal Transfer Printing:
In this process, ink is rolled off a ribbon using heat onto the label surface. It produces good print and long-lasting images. This is used for warehouse, factory, and outdoor long-lasting barcode labels.
Inkjet Printing:
Inkjet printers squirt liquid ink onto absorbent or coated surfaces. They yield rich color and fine resolution but are generally left for special designs or run lengths that are minimal. Water resistance is dependent upon ink and coating.
Laser Printing:
Laser printers use toner and electrostatic charge to produce sharp, smudge-free barcodes. They are ideal for on-demand printing in office environments or bulk production of document-integrated labels.
Flexographic Printing:
This process is used in industrial printing with flexible printing plates and is designed for high-volume label production. It supports continuous rolls, color print, and variable data insertion. Flexographic printing supports high adhesion and repeatable quality for high-volume packaging and product labels.
3) Durability and Environmental Resistance
Barcode labels must remain readable throughout their service life. The choice of material and printing method should match environmental conditions.
- Oil and Chemical Resistance: Resin-based ribbons with polyester or vinyl substrates deliver long-lasting readability.
- Abrasion Resistance: Protection coatings or lamination can protect barcodes from handling-intensive environments.
- UV and Sunlight Resistance: Outdoor labels must employ UV-resistant inks or coatings to avoid fading.
- Temperature Tolerance: High-temperature materials like polyimide or aluminum foil remain stable in manufacturing and electronics use.
4) Cost Differences and Selection Advice
Total barcode label cost is both dependent upon material and printing technology. Direct thermal paper labels are cheapest and most suitable for temporary identification. Applications requiring long-term use or industrial use are best satisfied by synthetic material combination and thermal transfer print, with best cost versus performance ratio.
Consider the expected lifespan, environment, and print volume when creating a labeling system. For example, a warehouse can use inexpensive direct thermal labels for daily shipments and heavy-duty polyester labels for asset tracking. Matching the durability of the label to its use ensures reliability and cost savings.

3. What are barcode labels used for?
Functioning of barcode labels is based on the symbology of the barcode itself and a reader capable of reading the symbols and interpreting them into valuable information, typically regarding the source of a product, cost, classification, and location.
When a bar code is scanned, the scanner feeds the data contained within it into an information system, usually a database of some sort. Barcode technology has given companies numerous advantages, such as the development of global distribution systems that operate smoothly and enable big companies like Walmart to maintain uniform product stock and price across the world.
Besides this, it has emerged as an important tool to enhance asset tracking and operational efficiencies for government ministries, small and medium enterprises, and hospitals. Firms utilize barcodes in several different ways including:
1) Monitoring Inventory
A fundamental inventory management system comprises software and a barcode scanner or mobile device. All the items of inventory, whether they are products in stock for selling, supplies, or raw materials, are marked with barcode labels. When a product is taken out of stock, a scan of the barcode merely decreases the count in the inventory tracking software, eliminating the need for typing an SKU by hand and the error possibility that is extremely common for grocery stores.
2) Tracking Assets
Every business, big or small, possesses IT assets and fixed assets. Barcoded asset tags are placed on all assets so that they can be easily checked in and checked out with asset tracking software. This method enhances accountability and simplifies audits.
3) Utilizing Barcodes for Return Mail
By incorporating a barcode on the return-mail registration postcard that corresponds to the product’s serial number, you can instantly track registered serial numbers. This eliminates the need for customers to locate and transcribe lengthy serial numbers.
4) Integrating Barcodes in Mail Merges
For company events, consider adding barcodes to RSVP cards to track responses accurately, without the challenge of deciphering handwritten responses.
5) Incorporating Barcodes in Invoices
Include a barcode showing the customer number or single invoice number on invoices. When they pay, the barcode is easily scanned to identify the customer account or invoice number, so incorrect issues such as crediting payment to an incorrect account or bill do not occur.
4. Types of barcode labels
The two broad types of barcode labels include linear, or 1D, and 2D. The most standard is the UPC (Universal Product Code), and it is one type of a linear barcode having two components: the barcode and a 12-digit UPC code. The manufacturer’s code number is the initial six numbers in the bar code and then five as the item number. The check digit, or the last digit, assists the scanner in checking whether the bar code read is valid.
Linear barcodes are generally capable of supporting encoding alphanumeric characters, thereby allowing presentation of varied textual information except for some special characters depending on the nature of the barcode. In contrast to that, 2D barcodes are more complex and can hold other information in the code, i.e., price, quantity, web addresses, or even images. Unlike linear barcode scanning, 2D barcodes require image readers to extract data hidden in it. Devices like camera phones, including Android and iPhone phones, are capable of reading 2D barcodes through their camera functions.
Having 2D barcodes greatly increased the number of barcode applications. Being able to carry additional information and easy to read for consumers with their mobile phones, 2D barcodes have more than tracking asset and inventory functions. In the contemporary period, 2D codes or QR codes can store up to 7,000 digits or 4,000 characters of text and enable companies to share information, websites, and video clips with customers, enable tracking of drugs for hospitals and medical centers, and combine data with programs like MS Office, MS SQL Servers, and other databases and files. Research a free QR code generator to create customized QR codes for your company.
5. How to Design Barcode Labels?
Designing a barcode label is work that requires precision and attention. A well-designed label allows scanners to read barcodes in any environment. The following principles cover the essential aspects of barcode label design from size to verification.
1) Size and Quiet Zone Guidelines
Every barcode must include adequate space around it called the quiet zone—a blank area that separates the barcode from surrounding text or graphics. This margin prevents the scanner from misreading nearby elements. Typically, the quiet zone must be at least ten times the X-dimension of the narrow bar or no less than 2.5 millimeters on either side.
The overall length of the barcode should be in proportion to the scanning distance. Barcodes which are easier to read are larger and vice versa. For tiny products or restricted label space, barcodes should be smaller. Reducing the barcode to below prescribed sizes may cause readability problems, especially when printed on irregular or glossy surfaces.
2) X-Dimension and Module Size Selection
The X-dimension defines the width of the narrowest bar in a barcode. It directly affects the resolution and scanning accuracy. Standard sizes are 0.19 to 0.33 millimeters for ordinary retail applications and can be increased to 0.5 millimeters for faraway industrial scans.
Selecting an X-dimension depends on the resolution of the printer and on the scanner hardware. High-resolution printers can handle small module sizes, but low-resolution or high-speed printers require the bars only a little larger than a small one in order to be readable. Uniform module width across the barcode ensures proper decoding.
3) Contrast, Colors, and Background Considerations
For proper scanning, there has to be contrast between the background and the bars. The ideal is black bars against a white background, but anything in dark-on-light will get by if it meets sufficient contrast ratio standards. Avoid using red, orange, or metallic inks for the bars, as most scanners use red light and thus might not scan them properly.
The background must be matte instead of glossy to avoid interference by reflection. Never put barcodes above images, gradients, or patterns in backgrounds because they will mislead the reader. Always print samples and test them under conditions of actual illumination where scanning will be done.
4) Placement and Scan Accessibility
The barcode should be located in a position where it will be reachable to be scanned upon handling or packaging. Common locations are the lower right-hand corner of product packaging or along an edge with a flat area. Barcodes should not be located near corners, curves, or irregular surfaces.
For logistic labels, picket-fence orientation (horizontal placement of the barcode) will more commonly provide better results than ladder orientation (vertical placement). For automated systems, ensure scanners cannot be obstructed from getting a clear line of sight and labels are directed in the direction scanning is expected.
5) Layout of Text, Icons, and Human-Readable Information
Barcodes stickers usually have additional information in the form of product names, serial numbers, or symbols. These must be placed on top of or below the barcode, but not over it. Employ readable fonts and put sufficient space so that the quiet zone is not mistaken for these details.
For compliance or industry purposes, the human-readable barcode data should immediately be below the code. Barcode readability is not obstructed when supplemental icons or safety signs are placed nearby but should not hinder readability. It aids in manual checking when scanning does not succeed.
6) Verification and Testing
Before mass production, all barcode designs are to be checked if they meet print quality and readability standards. Devices called barcode verifiers are applied in the measurement of parameters such as contrast, edge definition, and modulation. The tested values receive marks ranging from A to F relative to ISO/IEC 15416 or ISO/IEC 15415 standards.
In addition, early detection of potential problems can be achieved by using simulation software or test scans with handheld readers. Test barcodes printed from actual materials and printing process to incorporate surface texture and ink absorption. Spot checks during production occasionally to ensure consistency and avoid costly reprints or scan errors.
6. Barcode Label Replacement Strategies and Damaged Label Handling
Barcode labels are not fixed assets. Over a period of time, the friction, temperature changes, moisture, or chemical treatments will gradually reduce their readability. A structured replacement and maintenance plan ensures uninterrupted scanning accuracy and loss of data in business processes.
1. When to Replace Barcode Labels
Labels must be replaced if scanning performance declines or printed data begins to deteriorate. Fuzzy bars, missing segments, discoloration, or uneven scanning performance are typical symptoms indicating replacement. In most industrial or logistics settings, it is advisable to perform periodic inspection every three to six months depending on environmental exposure.
For labels on equipment or asset management that will endure for several years, using a replacement cycle along with yearly audits or maintenance can reduce unexpected breakages. When used in the presence of sunlight, oil, or cleaning chemicals, more regular intervals like quarterly replacements are typically necessary.
2. Preventive Replacement Strategy
To avoid disruptions, organizations can use a preventive replacement strategy. This involves tracking label age or scanning frequency in the database. Whenever a label crosses a certain threshold (e.g., one year on duty or some number of reads), a replacement order is triggered automatically. Preventive replacement ensures labels are legible before they expire from service.
Dual-labeling may also be used for high-value or mission-critical items. A redundant barcode in an alternate, hidden location is offered by a secondary barcode. When the primary label is destroyed, it serves as a backup in case it is damaged.
3. Handling Damaged or Unreadable Labels
In the event of partial damage or illegibility of a barcode label, the following remedies can be taken:
- Immediate Reprinting: If original data is still intact in the system, print a duplicate label with identical information. Carefully inspect the new print prior to its application to ensure that it is legible.
- Manual Data Retrieval: If scanning fails but human-readable text is intact, operators can manually input the code in order to avoid data disruption.
- Temporary Marking: In warehousing or logistics settings, a temporary handwritten or printed mark may be placed pending official replacement.
- Proper Disposal: Retire and destroy or dispose of illegible or expired labels completely to prevent confusion, especially with serialized barcodes.
4. Storage and Handling Precautions
To achieve maximum label life, keep unused labels in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and dust. Sheets or rolls must be kept flat or in the original wrapping to prevent curling. Surfaces used for application should be kept clean, dry, and oil- and residue-free to allow adhesives to bond securely and prevent premature peeling.
5. Record Keeping and Traceability
Maintaining a history of label changes helps to provide traceability and compliance with quality management systems. Date, accountable operator, and replacement reason can be recorded for each replacement activity. This data provides valuable insight into environmental wear patterns and helps refine future material or printing method selection.
7. Things to consider when choosing barcode labels.
There are things you need to consider when choosing barcode labels:
1) Environmental Resistance
Super-grade barcode labels are optimized to resist long-term exposure to UV, chemicals, abrasion, high/low temperatures, cyclic freeze/thaw, humidity, salt spray, and other environmental stresses.
2) Surface
Optimal adhesion is achieved on neat and smooth surfaces, rough surfaces being more difficult and potentially requiring the use of rivets or screws to fasten barcode labels. The surface material should also be taken into account as metal and plastic surfaces possess varying adhesion properties.
3) Size
X-dimension and barcode label size are very critical factors in maintaining barcode accuracy and machine readability. The X-dimension of a linear 1D barcode like Code 39 or Code 128 is the width of the thinnest bar in the symbol.The X-dimension within 2D symbols like Data Matrix or QR Code is the dimensions of one cell, both height and width. Our team at Express offers standard X dimensions and expert guidance on selecting the appropriate label size to uphold barcode quality and reliability.
8. How do barcode labels help businesses?
Barcode labels are an integral part of helping businesses become cost-effective and profitable. While barcodes themselves are needed, it is the procedures that they facilitate that in turn make businesses more efficient and less expensive.
Consider the Arizona Cardinals scoreboard team, who used an asset tracking system utilizing barcode technology to follow all parts necessary to have a hassle-free game day. The project realized a whopping saving of over 500 hours annually, showing a breathtaking increase in efficiency.
Whether you have a small business or find it difficult to source big equipment like projectors, barcode labeling and tracking of assets can automate processes and result in enormous cost and time savings for your company.
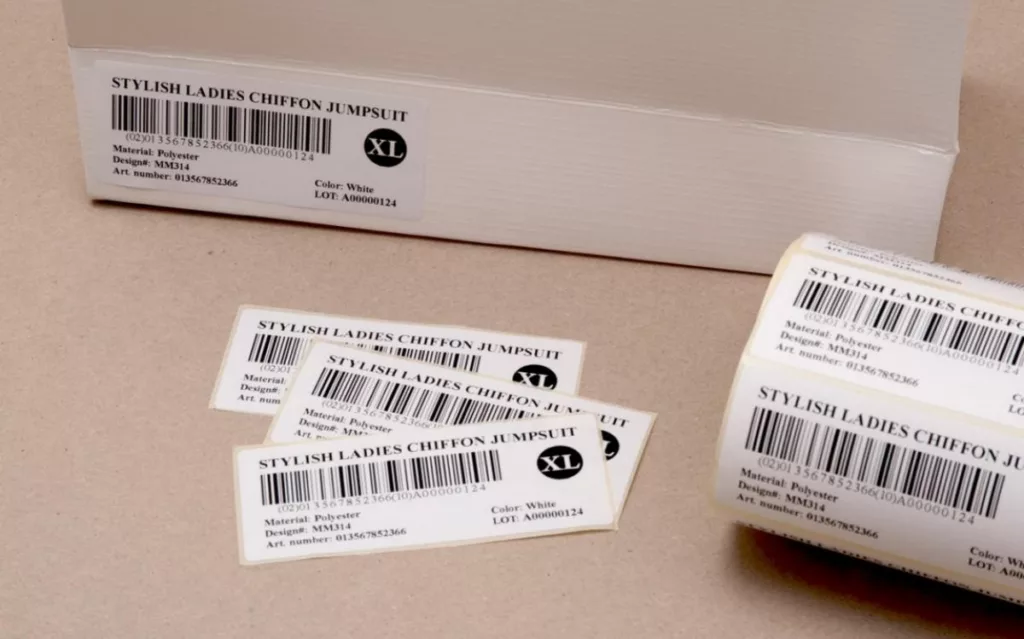
9. How to Find a Reliable Barcode Label Manufacturer?
Choosing a proper barcode label printer is as critical as label design. A trustworthy supplier guarantees consistent print quality, punctual delivery, and technical assistance throughout the long term. Because barcode labels have to fulfill precise scans and durability requirements, a qualified and well-equipped manufacturer has an immediate impact on the operational efficiency.
1. Evaluate Manufacturing Capabilities
Start with the technical capabilities and machinery of the manufacturer. A skilled barcode label factory should have the latest printing technologies such as thermal transfer, flexographic, and digital presses. Ask if they are capable of printing labels in other materials, paper, PET, PP, PVC, or specialty synthetics—and if they are able to provide coatings like lamination or varnish for extra protection.
If serialized printing, variable data, or QR codes are essential to your company, make sure that data integration and variable printing are enabled by the supplier. This is an important feature to inventory, logistics, and asset-tracking applications where each label holds varying information.
2. Check Quality Assurance Standards
A quality manufacturer follows strict quality control processes to ensure readability and durability. Look for companies that follow ISO 9001 or equivalent quality management certifications. Ask if they employ barcode verification systems (Grade A–D as per ISO/IEC 15416) to ensure contrast, edge sharpness, and scanning precision.
You should also look at how they test their materials with the types of conditions in your environment, such as moisture, heat, and abrasion, so that the labels will perform as expected.
3. Review Material Sourcing and Consistency
Consistent output demands consistent materials. Reputable manufacturers produce with good, high-quality sources of films, adhesives, and ribbons. They should be able to provide material data sheets that state composition, adhesive strength, temperature range, and life expectancy for each substrate.
Shun suppliers who are unsure of what their material sources are or whose material brand changes frequently since this may introduce variation in print density or adhesive performance between lots.
4. Assess Experience in Your Industry
Barcode label requirements differ across industries. Retail, logistics, manufacturing, pharmaceutical, and electronic device manufacturers will usually have industry-specific compliance expertise.
Cold-chain logistics labels, for example, need temperature-resistant adhesives, while medical labels need dust-free production with controlled alignment. Choose a supplier with sector-specific expertise in technical and regulatory requirements.
5. Evaluate Communication and Service Support
Good manufacturers do not just print, they consult professionally throughout. Good partners can help with label design, barcode checking, printer adjustment, and application advice.
Responsive communication is also vital. Consider how responsive the supplier is to queries, how effectively they communicate technical jargon, and if they can provide sample runs for testing prior to mass production.
6. Request Samples and Conduct Pilot Tests
Before signing a long-term contract, request samples or small production runs. Print legibility and barcode contrast are two areas to check with the provided samples. Adhesion and scratch/fade resistance should also be tested. Perform true scanning tests under the same conditions where the labels will be used.
Should the labels meet your operational specifications, proceed to a significant pilot order to confirm production consistency prior to full production runs.
7. Compare Cost Transparency and Delivery Performance
Cost alone should not determine your choice, but it must be transparent. A professional supplier will provide a detailed quotation that includes material cost, printing method, die-cutting, coating, and packaging. Avoid unusually low bids that may indicate lower-quality materials or insufficient inspection steps.
Delivery reliability is equally important, verify the manufacturer’s average lead time, production capacity, and on-time shipment rate.
8. Build a Long-Term Partnership
Once you identify a reliable supplier, you should set up a long-term cooperation arrangement. It is achievable to exchange design templates, printer parameters, and production specifications such that both can maintain similarity in serial orders. Long-term cooperation leads to cost savings, faster reorders, and quality consistency.
In summary, a quality barcode label maker has to assemble strong manufacturing capability, continuous material supply, quality control certification, and expert communication. By investing time in thinking about all of these elements, you can build a long-term relationship that will see your barcode labels being accurate, durable, and affordable throughout their lifespan.
10. Barcode Labels FAQs
1. Why does barcode scanning sometimes fail?
Scanning barcodes often fail due to issues of print quality, contrast, damage, or design. Some of the causes are:
- Insufficient print contrast between background and bars, especially where colored inks or glossy surfaces are employed
- Incorrect margins of quiet zones or distortion of bar widths through scaling during printing
- Poor material choice, e.g., reflective or embossed surfaces which make scanner light scatter
- Label damage, e.g., scratches, creases, or dirt accumulation
- Incorrect alignment of the barcode relative to the scanner beam
To prevent these issues, follow design recommendations, employ high-quality ribbons or ink, and perform regular verification tests on a barcode verifier or scanner.
2. How can printing and material costs be reduced?
There are numerous methods to control cost without compromise on performance:
- Coordinate material and usage time: Apply paper labels for short-time usage and synthetic material for long-time or abusive conditions only.
- Optimize label size: Utilize the most compact readable barcode size to save material waste.
- Standardize layouts: Use standard label templates to decrease design and cutting setup expenses.
- Leverage batch printing: As volumes rise, cost per unit falls as setup and calibration expense are divided.
- Select efficient printing methods: Thermal transfer printing is cost-effective for long-term outcomes, while direct thermal printing is ideal for short-term labels.
Working with a skilled manufacturer can also help identify cost-effective material substitutes without sacrificing readability of the barcodes.
3. Can one label include multiple languages or barcode types?
Yes. The majority of multinational companies utilize multi-language and multi-code designs to make it easy for international logistics or multilingual packaging. A single label can have:
- Product descriptions and safety warnings in multiple languages
- One or more barcode types (e.g., EAN-13 for retail, Code 128 or QR for internal tracking)
When stacking two or more codes, keep distinct spacing between each barcode’s quiet zones to prevent interference. Give each barcode enough size and contrast for independent reading.
4. How can barcode labels perform in extreme environments?
In high-temperature, humidity, cold storage, or chemical exposure environments, it is essential to select materials and ink suitably:
- Apply polyester (PET), polypropylene (PP), or polyimide substrates for enhanced heat and moisture resistance
- Use friction and chemical cleaning-resistant resin-based ribbons for thermal transfer printing
- Use laminated or coated surface for UV light, oil, or solvent resistance
- In cold-chain logistics, select freezer-grade adhesives that are capable of remaining flexible at low temperatures
Pretest sample labels under real-world environmental conditions prior to final production to qualify for durability and scanning accuracy.
5. How are urgent or small-quantity orders handled?
A few manufacturers offer on-demand or digital printing capacity for small print runs or express orders. Digital printing allows variable data and barcodes of different types without the cost of physical printing plates. For fast projects:
- Provide finished design files in vector format to reduce preparation time
- Confirm materials in stock before ordering
- Purchase express production and shipping levels
- Utilize simplified finishes such as matte coating rather than lamination to reduce turnaround time
Having a partnership with a reliable supplier ensures faster response to short-term labeling needs as they can keep your design templates and material specifications on hand for repeated orders.

11. Conclusion
Sufficient barcode label design is an exhaustive process with meticulous attention to detail and strict adherence to industry best practices in label design, print, and data encoding. Through harnessing the capabilities of barcode label printers and strict adherence to the professional standards provided in this definitive guidebook, businesses are able to create state-of-the-art barcode labels that maximize efficiency, accuracy, and productivity in inventory tracking and management protocols.
From producing store product labels, shipping package barcodes, to tracking assets, the implementation of these practices will make barcode labels a consistent set of tools to automate business and drive success




Leave A Comment